IPS
Child Nav IPS - How It Works
What makes Child Nav a superior solution is its Integrated Pediatric Screening (IPS). IPS is a recommended result of the Help Me Grow (HMG) Pediatrics Supporting Parents (PSP) grant funded by the Silicon Valley Foundation. Child Nav takes conventional IPS a step further using an AI-based probability network to administer an evidence-based IPS Developmental Checkup. The IPS Developmental Checkup integrates standard screenings like the ASQ®, M-CHAT™-R, etc. into a single comprehensive assessment that drives effective actions as its result. To do this each standard screening is broken into its component measures and question items, and organized into a probability network of nodes. Probabilistic Administration and Scoring (PAS) is used to traverse the probability network asking questions and arriving at effective actions.
Probability Networks
Using a probability network to implement the IPS Developmental Checkup, we group the network nodes into Primary Scan Nodes, Triggered Secondary Nodes and Actions Nodes. The strategy is to use Primary Scan Nodes to find symptoms of underlying concerns that are in turn measured using Triggered Secondary Nodes. Action Nodes then address the symptoms and concerns, along with setting expectations for normal health and development, engaging, connecting and initiating follow up actions. The diagram below illustrates the IPS Developmental Checkup probability network used for preschool children 0 to 5 years old.
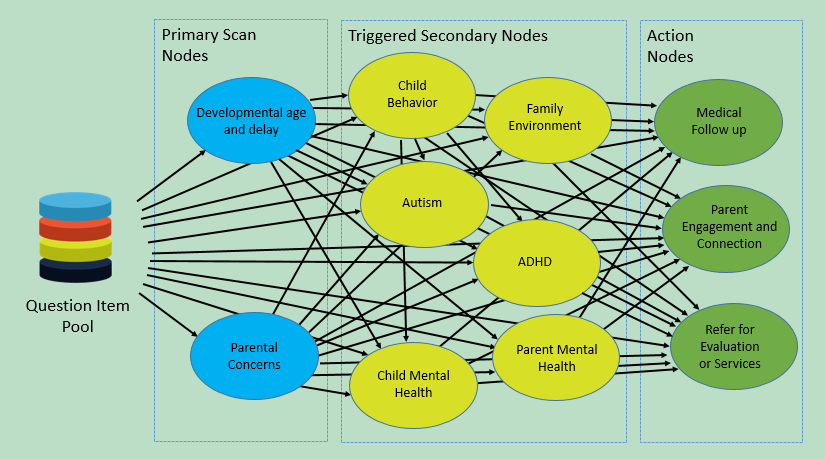
Each node operates independently, is age-based and uses information from previously administered questions and measures when available. As a result any node can be enabled or disabled using configuration settings to control the breadth and depth of information gathered using the probability network. For example if all you need to administer is a standard ASQ, you can disable all the Triggered Secondary Nodes and Action Nodes and set the Primary Scan Nodes to use the ASQ.
PAS - Probabilistic Administration and Scoring
PAS is a patented methodology for implementing probability networks. Based on Item Response Theory (IRT) and probabilistic evidence from normative data, the methodology is fundamentally evidence-based. Not having access to computing capabilities, conventional paper-based screenings are static, generally requiring more questions to make the same measurement. Additionally, conventional hand scoring is inherently less accurate creating more false-positive and false-negative results. PAS performs far better and is used in all Child Nav products.
Probabilistic Administration
Probabilistic administration provides the practical answer to “Which question next?” It is used to adequately administer each node using the least number of questions possible. In the process it uses
- Configuration settings to select which standard screenings to enable
- Probabilistic scoring to compute prescreen measures based on probabilistic evidence from previously asked questions and computed measures
- Node logic to apply configuration settings, age constraints, prescreen trigger thresholds and select which question to ask next
Probabilistic Scoring
Every link in a probability network is based on normative probabilistic evidence from question items and computed measures. A major advantage of using probabilistic scoring is that it performs better as more normative data is generated and applied. Probabilistic scoring is used
- To compute prescreen measures for probabilistic administrations
- As an alternative method to compute standard screening measures based on the screening question items
- To enable different standard screening measures to interchangeably use a common measurement scale
PAS Version of ASQ
With permission we have developed a PAS version of ASQ. A date-of-birth rather than age group is all that is needed to get started. The PAS methodology asks a minimum number of questions when there is no delay detected and as many questions as necessary when there may be concerns. Probabilistic scoring makes it more accurate than conventional scoring and dynamic probabilistic administration provides a greater depth of information to explore concerns. Based on a common developmental age measurement, the methodology is the same as that used for CDC-DMC and SWYC as well.
Developmental Age as a Measure
A major challenge for ASQ, CDC-DMC and SWYC is how to accurately measure developmental delay. Additionally the CDC-DMC used in the CDC “Learn The Signs. Act Early.” (LTSAE) program was not developed with a scoring solution. PAS meets this challenge computing a common developmental age in each development domain being measured in the standard screenings. For example the ASQ measures communication, fine and gross motor, cognitive and social-emotional domains, each having a developmental age measured in months. These ages can be compared to the physical age of the child to measure developmental delay in each domain directly in months as well. By comparison the CDC-DMC lumps fine and gross motor into a single motor domain keeping the others and the SWYC lumps all the developmental domains into a single developmental age measurement.
Using PAS to compute developmental age, each question item is effectively a milestone with an item age where an average child can perform the specific milestone. This enables each standard screening’s question items to be organized into an ordered list and used in the probabilistic administration’s node logic to compute which question next. Using a common developmental age scale and a common PAS administration strategy enables apples-to-apples comparison and interchangeability between the different standard screenings.
Comparing ASQ and CDC-DMC
When you compare ASQ and CDC-DMC the result is that a PAS administered ASQ performs better than a PAS administered CDC-DMC and they both perform significantly better than a conventional ASQ. If you are using a conventional ASQ, you definitely want to use the PAS version of ASQ, or at least add PAS scoring, there is no extra cost. If cost is a consideration, you may want to switch to a PAS administered CDC-DMC which is public domain and will perform considerably better than what you are doing now. Child Nav standard products use the public domain CDC-DMC (CDC-based) and premium products use the licensed ASQ (ASQ-based). Either way you want to convert to measuring developmental age and take advantage of the breadth and depth of the Child Nav IPS Developmental Checkup.
Node Measures
Standard screening measures are age-based and organized into nodes. Specific measures are enabled by default based on the standard configuration being used. These configuration settings can be easily adjusted to meet your needs.
ASQ-3
Nodes: development, parental concerns
Measures: communication, gross motor, fine motor, cognitive, social emotional, parental concerns
CDC-DMC
Nodes: development
Measures: communication, motor, cognitive, social emotional
SWYC
Nodes: development, child behavioral, parental concerns, family environment
Measures: developmental milestones, inflexibility, irritability, routine, social interaction, parental concerns, family questions
ASQ:SE-2
Nodes: child behavioral, parental concerns
Measures: self-regulation, communication, adaptive functioning, autonomy, affect, interaction with people, parental concerns
M-CHAT-R
Nodes: autism
Measures: autism risk
Vanderbilt ADHD
Nodes: ADHD
Measures: inattentive, hyperactive/impulsive, combined, oppositional-defiant …
PEARLS
Nodes: child mental health, family environment
Measures: part 1 severe stress, part 2 environment
PCL-C
Nodes: child mental health
Measures: trauma/PTSD
EPDS
Nodes: parent mental health
Measures: parent postpartum depression
PFS
Nodes: family environment
Measures: protective factors – family functioning/resiliency, social supports, concrete supports, child development/knowledge of parenting, nurturing and attachment
ESQ
Nodes: family environment, parental concerns
Measures: education, housing, child family health, economic/financial, family life, communication
Child Nav Items
Nodes: parental concerns and goals, trigger logic and items
Action Nodes
Effective actions break down into parent-facing and provider-facing, and are driven by what has been discovered during an IPS Developmental Checkup administration. There are 3 levels of actions supported:
- actions supporting health and development
- actions addressing identified concerns
- actions managing identified medical, psychological and special needs
Additionally each Child Nav solution has different levels of provider support requiring different levels of parent involvement to best support each child’s needs.
Parent Actions
Parent-facing actions can be carried out through the Child Nav IPS Developmental Checkup parent report, automated touchpoint messaging and linkage to educational materials, resources and services.
- Actions supporting health and development include: development promotion; milestone tracking grouped by accomplished, working on and expected next; age appropriate activities; educational messaging and access to educational materials about what to expect next.
- Actions addressing identified concerns include recruitment and encouragement to address concerns; concern specific activities; educational messaging and access to educational materials targeting concerns; and linkage to appropriate resources and services.
- Actions managing identified medical, psychological and special needs are highly depend on the resources and services that are available and include linkage to appropriate resources and services; recruitment and encouragement to follow through on flags and referrals for evaluation and services; automated follow up to ensure referrals are taken and services are utilized; educational messaging and access to educational materials specific to identified flags and referrals.
Provider Actions
Provider-facing actions can be carried out through the Child Nav IPS Developmental Checkup provider report, provider discussions with parents and referral and linkage for the parent to resources and services.
- Actions supporting health and development include promoting parent awareness and involvement in their child’s development; milestone tracking and discussion with parents; recommendation of age appropriate activities; providing educational messaging and access to educational materials about what to expect next
- Actions addressing identified concerns include discussion with parents about their concerns, as well as other identified concerns; recruitment and encouragement to address concerns; recommendation of concern specific activities; provide educational messaging and access to educational materials targeting concerns; and provide linkage to appropriate resources and services.
- Actions managing identified medical, psychological and special needs are highly depend on the resources and services that are available and include providing, or linking to appropriate resources and services; parent recruitment and encouragement to follow through on referrals for evaluation and services; automated follow up to ensure referrals are taken and services are utilized; provide educational messaging and access to educational materials specific to identified flags and referrals.
